Introduction
This page is designed to get you familiar with Promethium in less than 5 minutes.
Architecture
Promethium utilizes a hybrid application architecture.
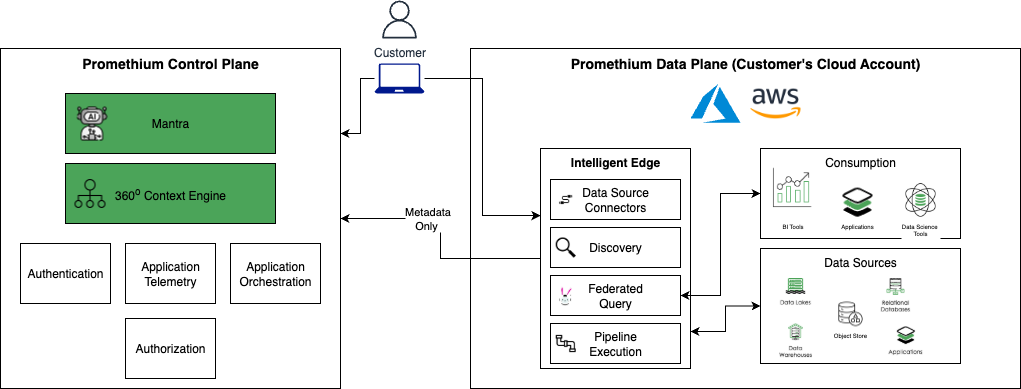
Promethium Control Plane
The Promethium Control Plane is hosted and managed by Promethium. The scope of the control plane is;
- Authentication
- Metadata
- Promethium’s agentic layer
- Application orchestration
- Application Telemetry
Promethium Data Plane (Intelligent Edge)
The Promethium Data Plane is installed within the customers cloud provider as a private cluster. The data plane has connectivity to all data platforms. This ensures all data remains within the customers private network. Data exposed to an end user flows directly from the data plane to the users browser requiring all users to be part of the the customers private network. No data is exposed to the Promethium Control Plane. Customer is responsible for the management and monitoring of the Data Plane infrastructure. Promethium is responsible for the Application layer management and monitoring. The scope of the Data Plane is;
- Data Platform Connections
- Metadata Discovery
- Federated Query
- Pipeline Orchestration
- Data APIs
Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Datamap | A Datamap is a virtual or materialized data artifact within Promethium that represents a business-relevant dataset defined through heterogeneous SQL. Each Datamap includes a name, description, and a SQL definition executed via Trino, enabling queries across disparate data sources such as Snowflake, Databricks, SQL Server, and more. Datamaps can be:
|
| Published Datamap | A Published Datamap is a Datamap that has been instantiated as a view in Trino or as a physical table in a target data platform through the Publish action. Publishing makes the Datamap queryable by other users and systems, and—if materialized as a table—automatically managed via pipeline orchestration to stay in sync with its source logic on a defined refresh schedule. |
| Domain | A logical grouping objects such as Datamaps, tables and views to allow easier operational management e.g. application of access control rules |