Version Control
Version Control
Version management in Promethium allows users to safely edit, test, and instantiate Datamaps without risking accidental changes to production logic.
Why Version Control Matters
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Safety | Prevents overwriting production logic with untested changes. |
| Accountability | Tracks who instantiated what and why through descriptions, timestamps, and authorship. |
| Reproducibility | Enables referencing prior versions for debugging or auditing. |
| Collaboration | Multiple editors can iterate on Datamap changes without interfering with live logic. |
User Roles & Permissions
| Role | Permissions |
|---|---|
| Viewer | View Instantiated Versions, Cannot instantiate versions, Cannot edit SQL |
| Editor | Edit Datamap SQL, Instantiate new versions, Promote Datamaps |
| Owner | Full access, Manage permissions, Delete Datamaps |
Workflow
This workflow describes how Datamaps are edited, tested, instantiated, and migrated across versions.
Create the First Version of a Datamap
Users can create a fresh datamap and click on New Version and then Instantiate to create a fresh version.
Instantiation Types
| Instantiation Type | Definition | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Table | A fully materialized physical table stored in the warehouse. | Heavy analytics, Repeated queries, Downstream pipelines |
| View | A virtual table defined by SQL; no data physically stored. | Lightweight logic, Real-time data access |
Each instantiated view and table becomes a destination of the Datamap.
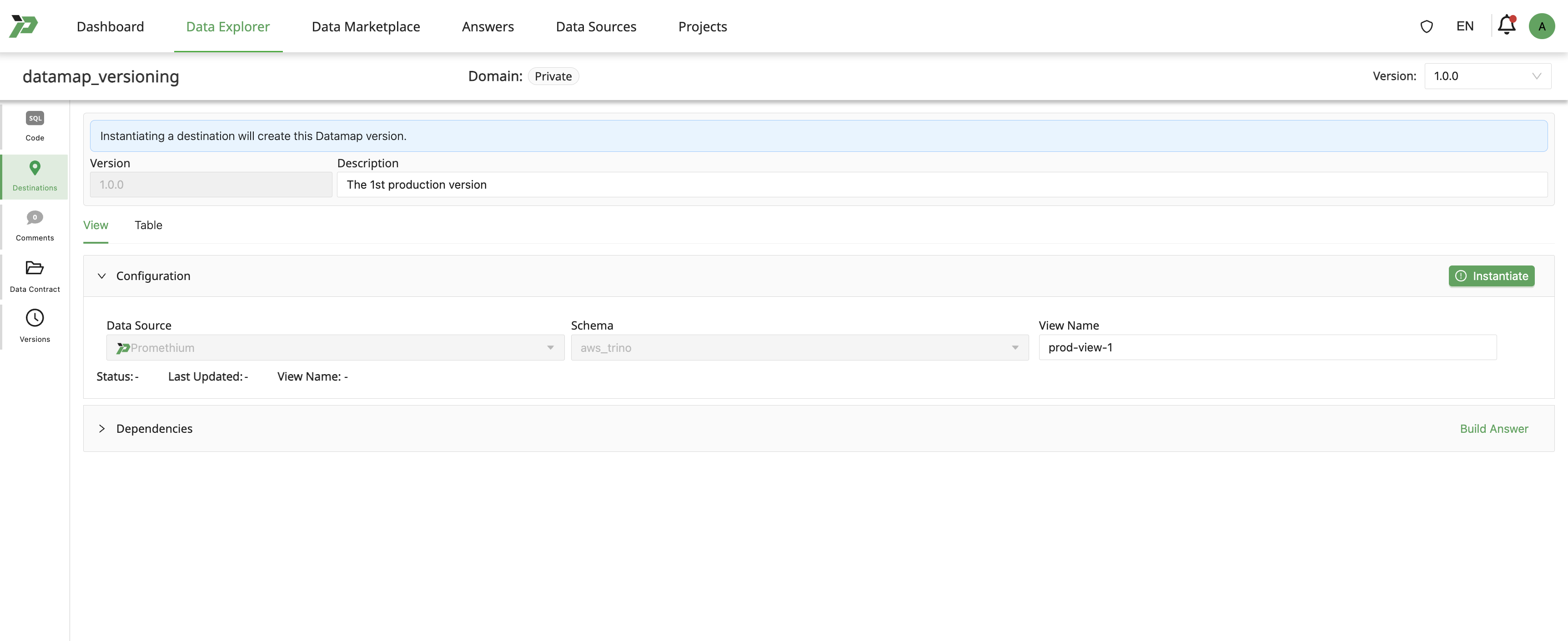
1: Initiate Instantiate
User add new version number.
2: Description
User provides a description of the changes.
Example: “The production version for customer orders with optimized pricing.”
3: Instantiating
User can click on Instantiate to create a version.
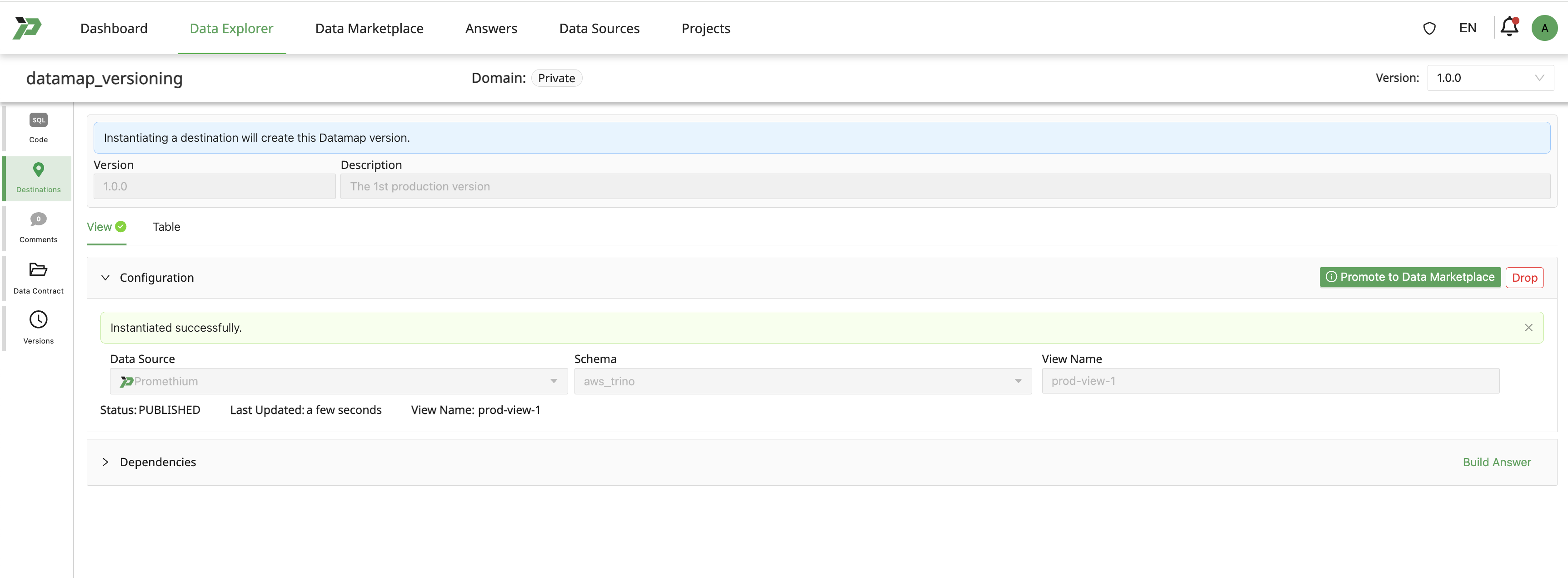
Post creating the first version successfully status is shown as PUBLISHED.
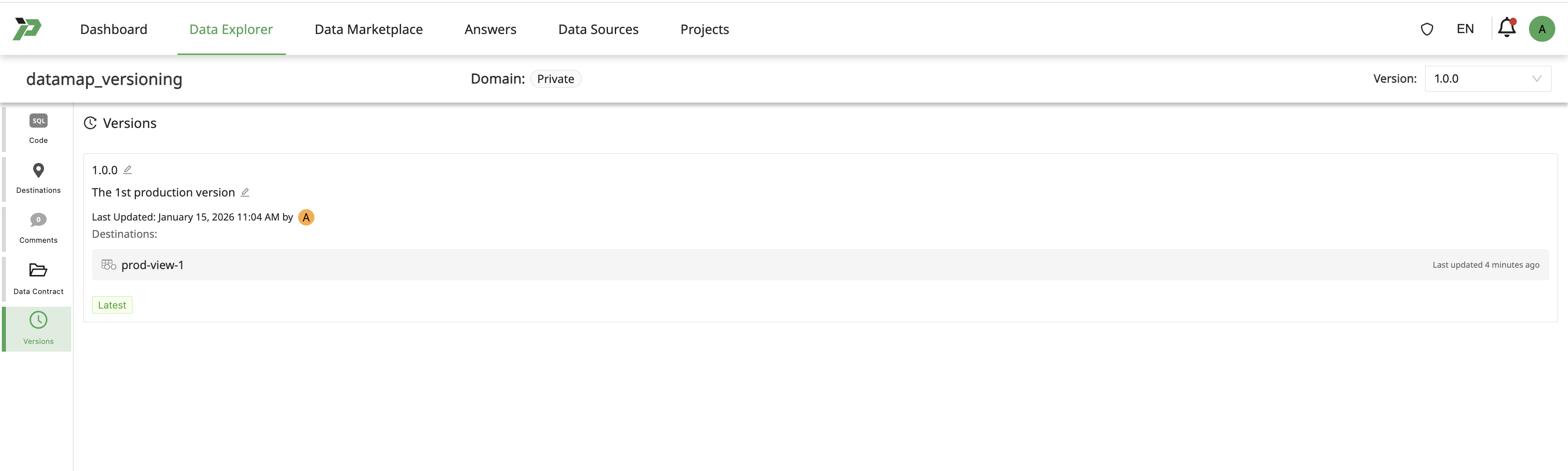
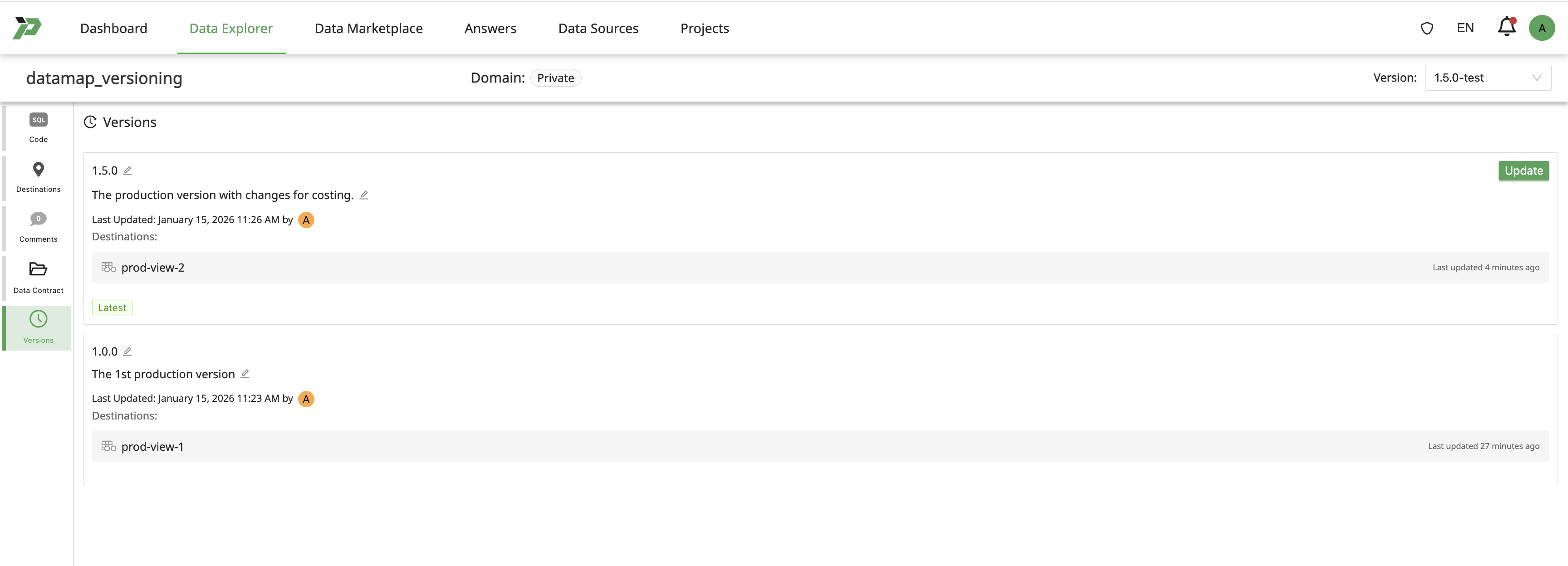
Click on Versions tab to list the available versions.
Edit the Latest Version of a Datamap
Users can begin by editing the latest instantiated version of a Datamap (not older versions).
Edits can be made in either of the following areas:
- Datamap SQL
- Datamap tables and columns, including:
- Aggregations
- Conditions / filters
- Joins
- Column treatments and transformations
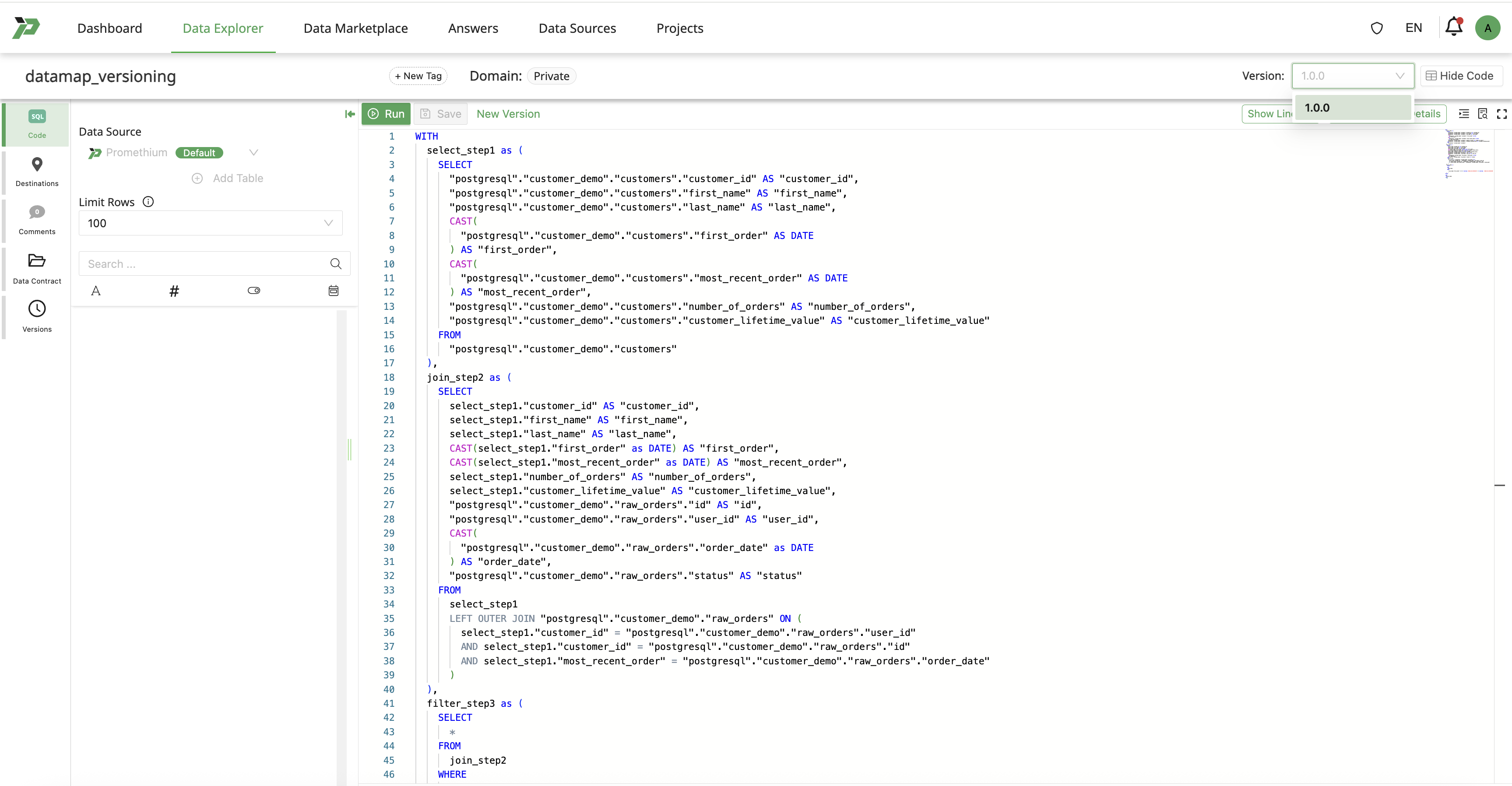
Any change made will create a draft state of Datamap, without affecting the currently instantiated version.
UI Indicators
-
Blue banner: “Saved as Draft. There are no changes to existing Datamap versions nor instantiated objects.”
-
Version selector displays Draft and this indicates the Datamap state as Draft.
-
The draft state of a Datamap:
- Is editable
- Is not yet visible as a Marketplace-ready asset
- Does not impact existing consumers using the instantiated version
Users may continue iterating on the draft state of Datamap without restriction.
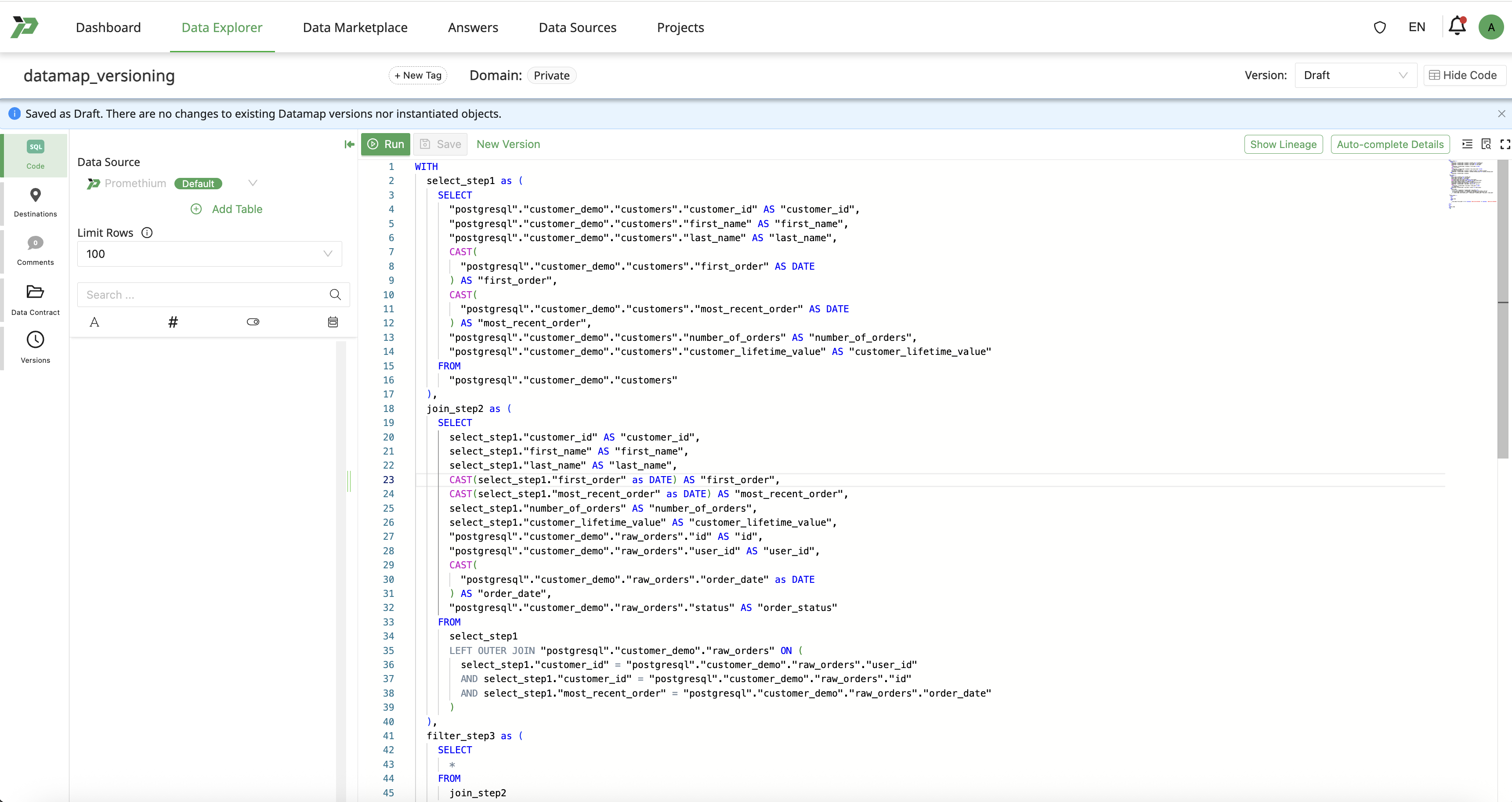
Instantiate a version for testing from Draft state of a Datamap
Click on New Version and then Instantiate to create the next version for testing.
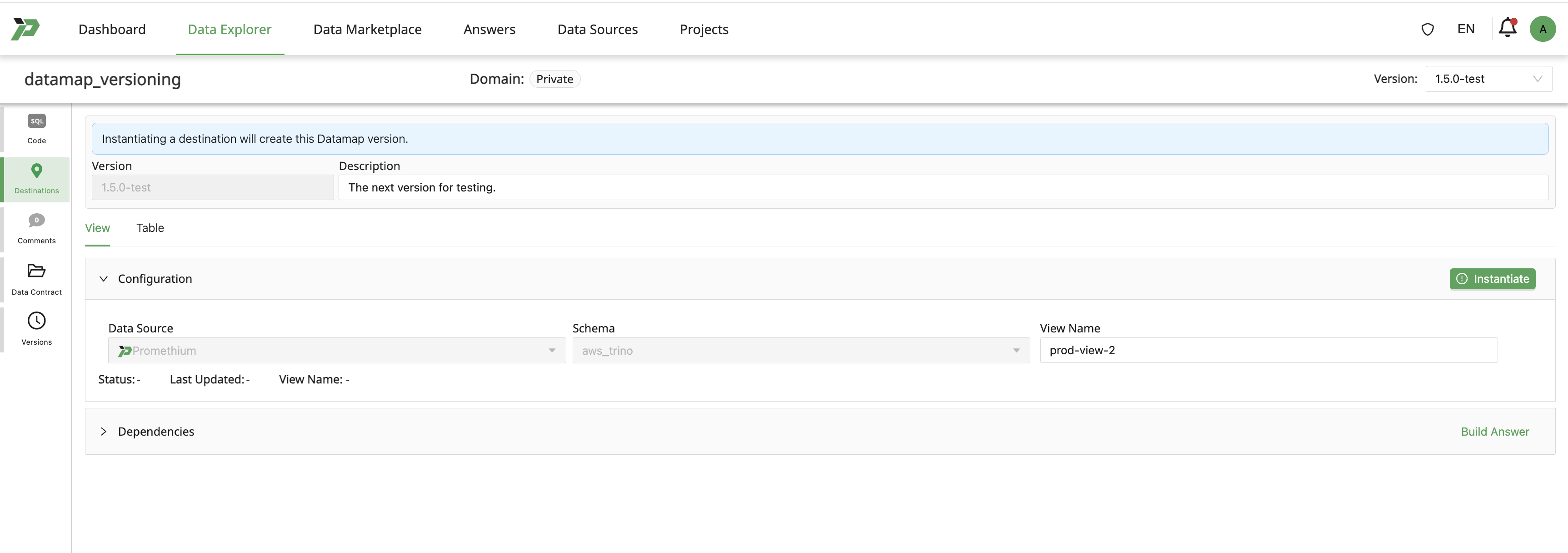
Rename the test version for production usage
Go to the list of version.
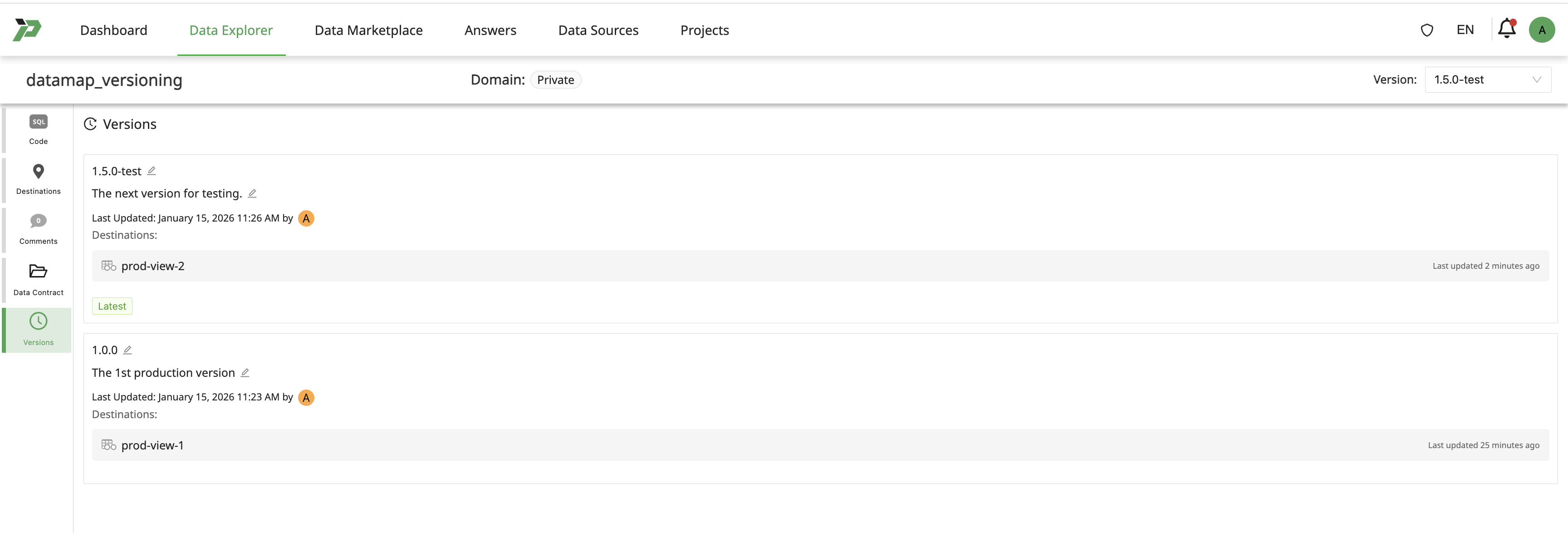
Rename version & update description to migrate the test version for production usage.
Drop Instantiation
Overview
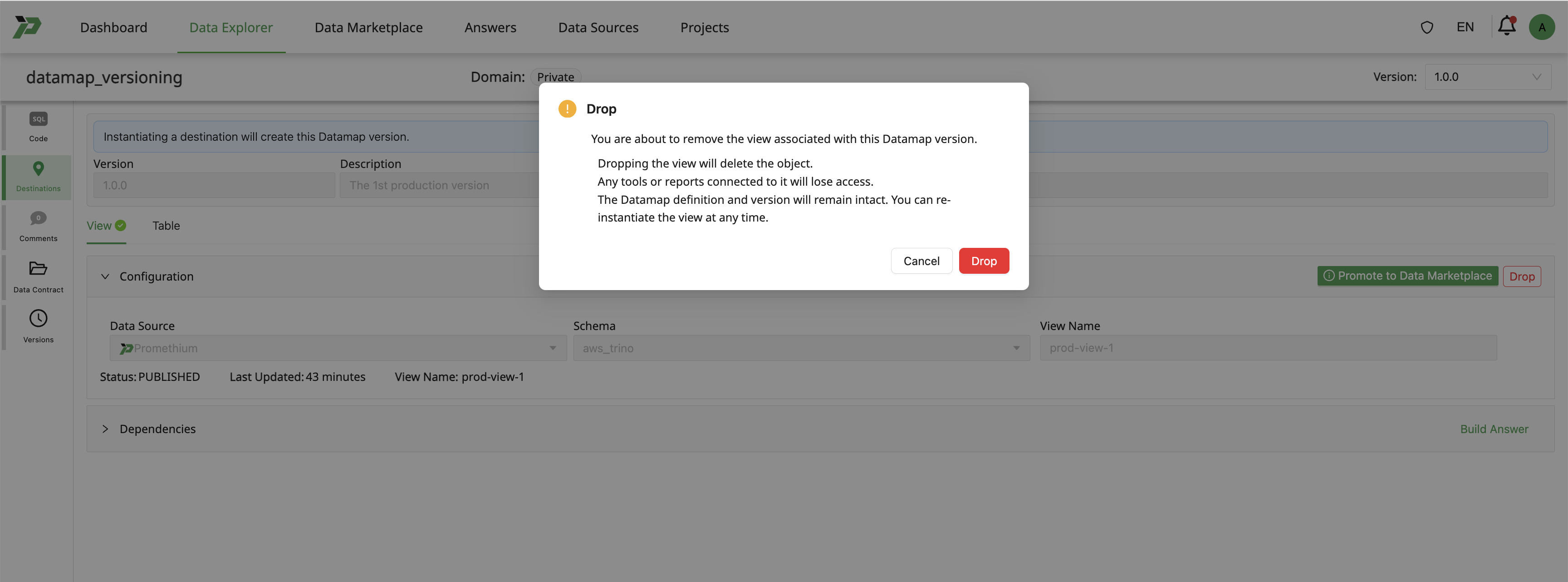
Drop Instantiation removes an instantiated version of an object from the active execution environment.
This action is used to retract a deployed instance that is no longer valid or needed, while maintaining the Version.
Behavior
When an instantiation is dropped:
- The instantiated object is no longer queryable
- Downstream dependencies will surface warnings or fail
- Version will remain intact.
What This Does Not Do
Dropping an instantiation does not:
- Automatically instantiate another version
Governance
Only authorized users may drop an instantiation.
Only one instantiation may be active at a time. Dropping it returns the object to a non-instantiated state.
Destinations and Version Visibility
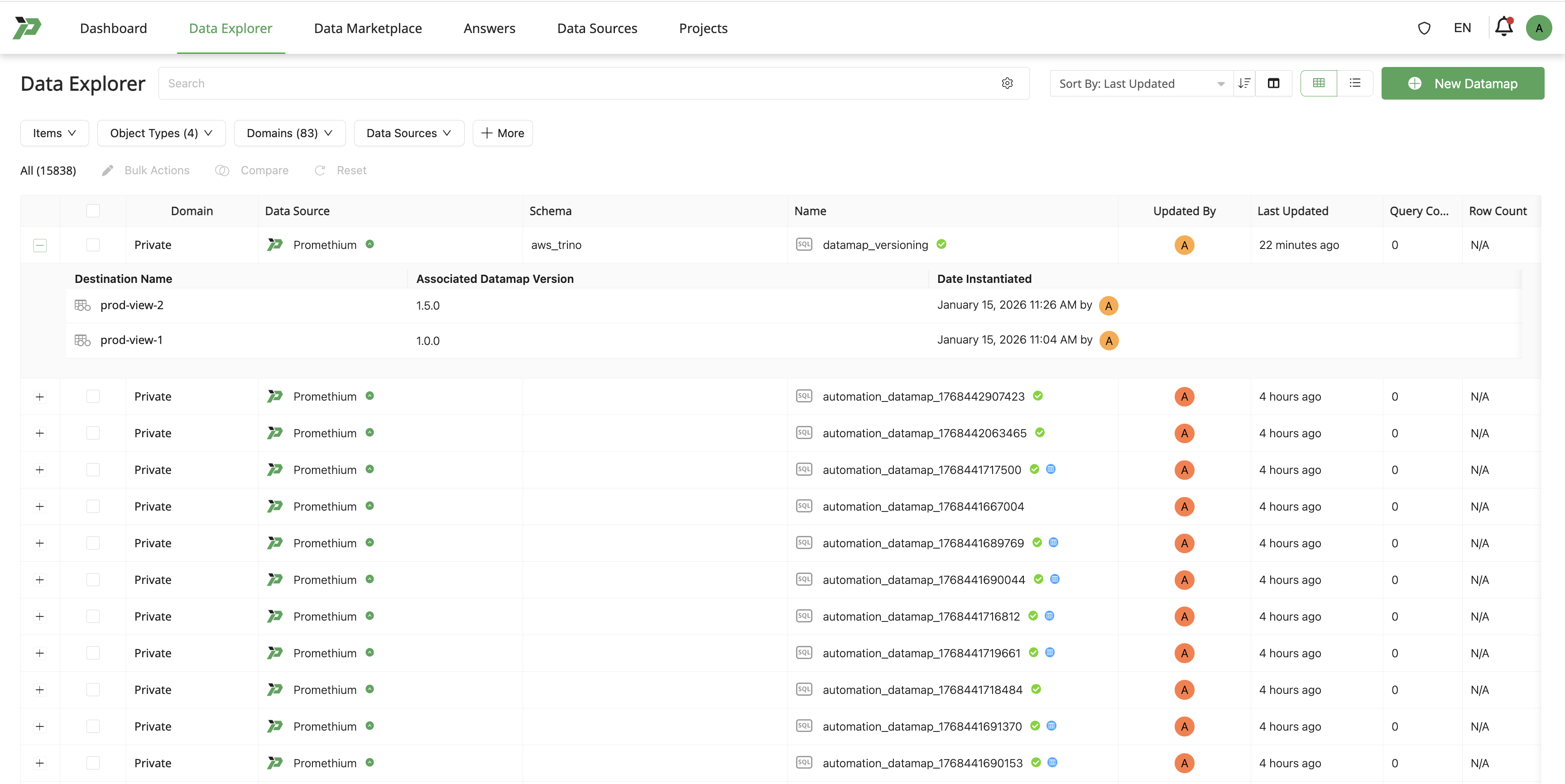
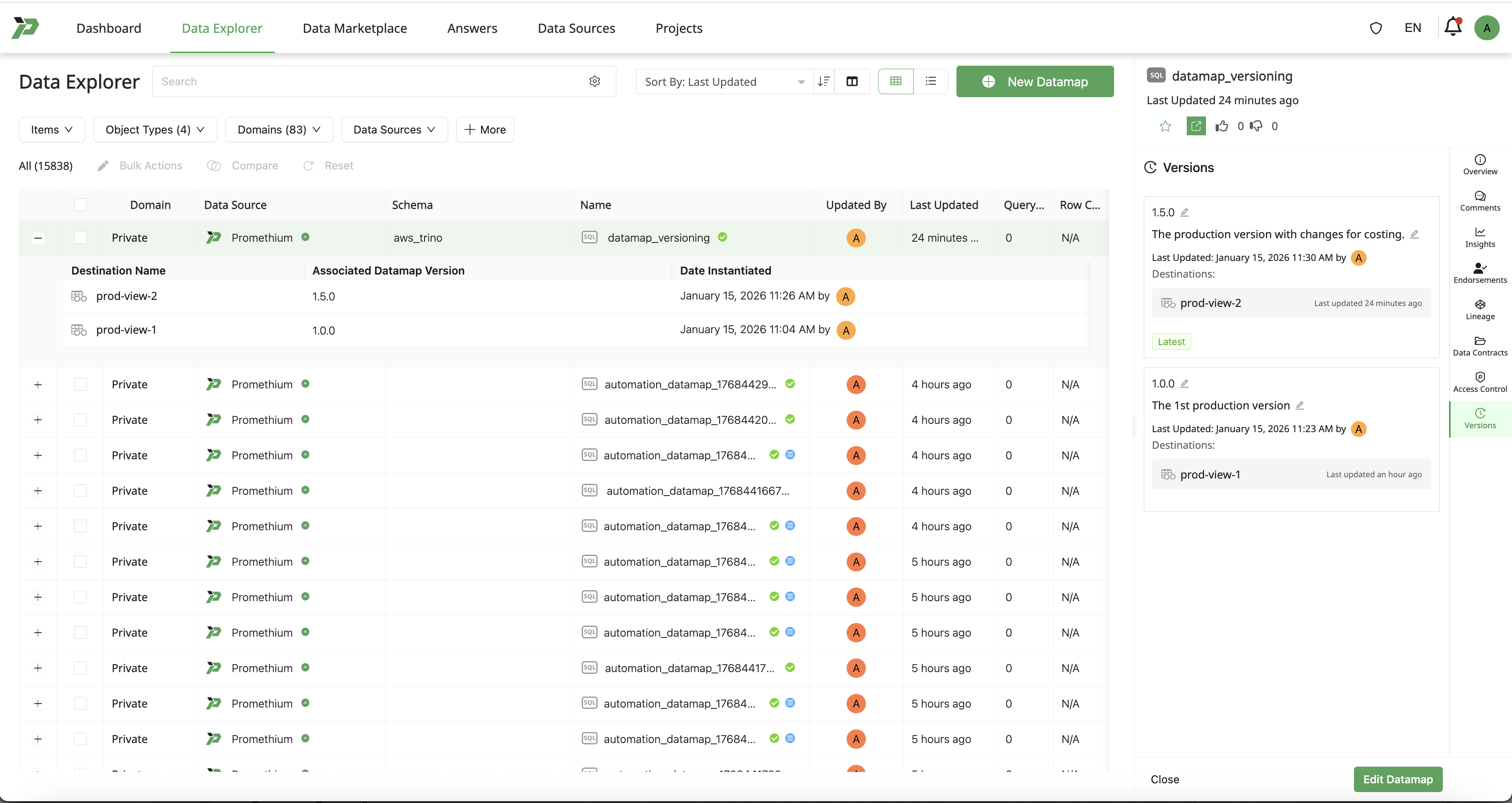
In the Fabric UI:
- All destinations (tables and views) are displayed as:
- Destinations of the Datamap
- Associated with the Datamap version that created them
- Users can clearly identify:
- Which version produced which destination
- Which destinations are currently active
Deprecation and Migration (Partial Support)
Consumers may choose to migrate to the newly instantiated version over time.
- Marking a previous version as deprecated is not currently supported in Fabric.
- Migration is handled operationally by consumers switching to the new destinations.
Once migration is complete:
- Consumers may drop the destinations (tables/views) associated with the previous version.
- The Datamap version and its metadata are retained indefinitely for:
- Audit
- Lineage
- Compliance purposes
Best Practices
- Always include meaningful instantiate descriptions.
- Reference version numbers in documentation and handoffs.
Key Features Recap
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Datamap in a Draft State | Prevents accidental changes to production logic. |
| Multi-Step Instantiating | Ensures intentional, documented version releases. |
| Instantiation Options | Table or View for production workflows. |
| Version History | Easy comparison of prior logic for debugging and governance. |
| Change Protection | Preserves unsaved edits and prevents data loss. |