Data Authorization
Data Authorization provides fine-grained access control to data objects (tables, views, datamaps). This complements UI permissions by enabling precise control over who can access specific data assets.
Effective Permissions
A user can access a data object in a Promethium UI if they have both:
- UI permission - The Permission Set allowing access
- Object permission - Access to the specific object
Example:
User: Sarah
Role: Data Engineer (includes "create_datamap" permission)
Domain: Marketing (Editor access)
Result: Sarah can create datamaps and has Editor access to datamaps in the Marketing domain
Sarah cannot access datamaps outside the Marketing domain
Access Control Mechanisms
1. Object Ownership
When a user creates an object, they automatically become its Owner with full control:
- View, edit, delete the object
- Grant access to other users or roles
- Change ownership
- Manage object-level permissions
Ownership is automatic - No explicit permission grant needed.
2. Access Grants
Data Access Privileges take the form
user privilege object.
user can be an individual user or a group of users that have been assigned to a role.
object can be an individual object or a group of objects that have been assigned to a domain.
Access Levels
Data objects support three access levels:
| Level | Capabilities | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| Owner | View, edit, delete, grant access, transfer ownership, change domain | None |
| Editor | View, edit, grant access, change domain | Cannot delete or transfer ownership |
| Viewer | View metadata, query data, export results | Read-only, cannot modify or grant access |
Users receive access through: object ownership (automatic for creators), direct grants, domain membership, or role-based domain access.
Managing Data Access Privileges
Create a Data Authorization privilege through the Data Authorization interface (shield icon in the header, shown below).
Navigation:
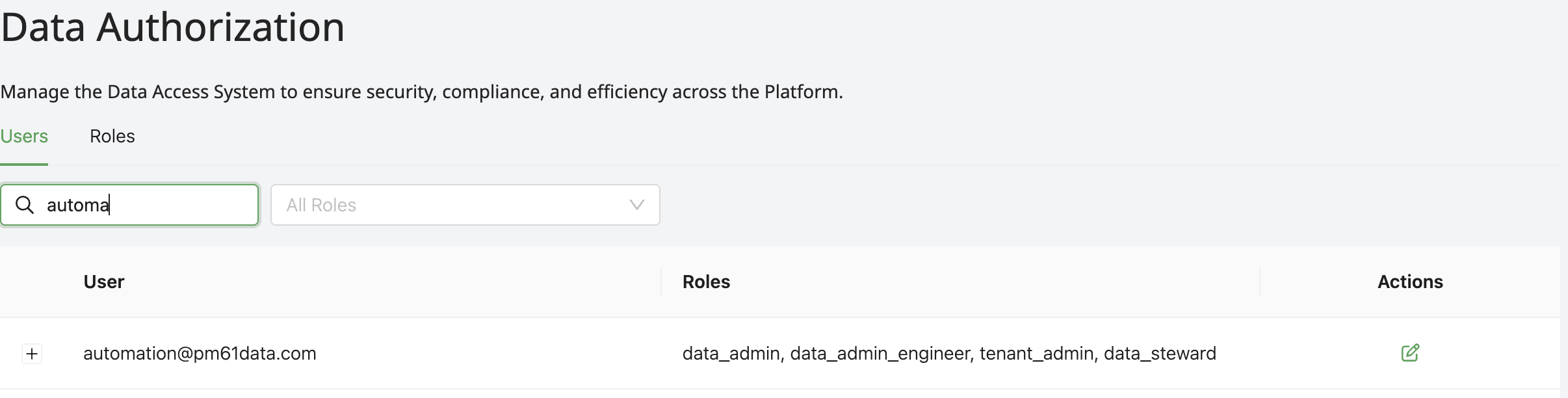
- Navigate to Data Authorization menu item
- Select the Users or Roles tab
- Choose a User or Role to configure
- Click the Edit button
- + Add Privilege button - Add new Data Authorization privilege
- Choose Domains or Add Individual Object Privilege
- For a Privilege assigned to a Domain
- Select a Domain
- Choose - Access Type - Access level (owner, editor, viewer)
- Save the Privilege
- For a Privilege assigned to an Individual Object
- Select a Data Source, Schema, and Object
- Choose - Access Type - Access level (owner, editor, viewer)
- Save the Privilege
Removing Data Access Privileges
To revoke a user's or role's access to an object:
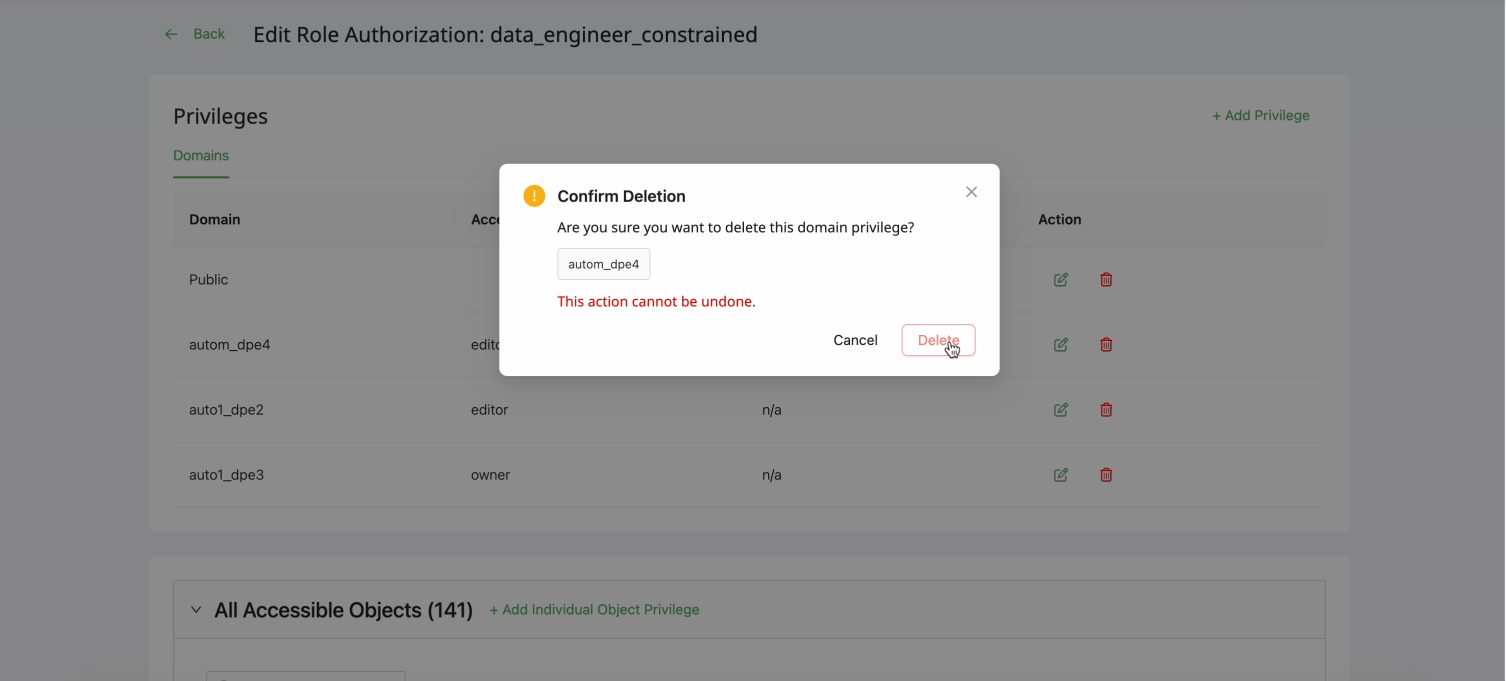
- Navigate to Data Authorization menu item
- Select the Users or Roles tab
- Choose the user or role to modify
- Find the Data Access privilege to remove
- Click the Delete (trash) icon in the Action column
- In the confirmation dialog, review and click Delete
The "All Accessible Objects" count updates immediately to reflect the reduced access.
Row-Level Filtering
Apply row-level filters to restrict which data rows users can see within a table or datamap. Row-level filtering adds a WHERE clause to queries automatically, limiting visible rows based on user attributes or object permissions.
Configuring Row Filters
From Data Authorization Interface:
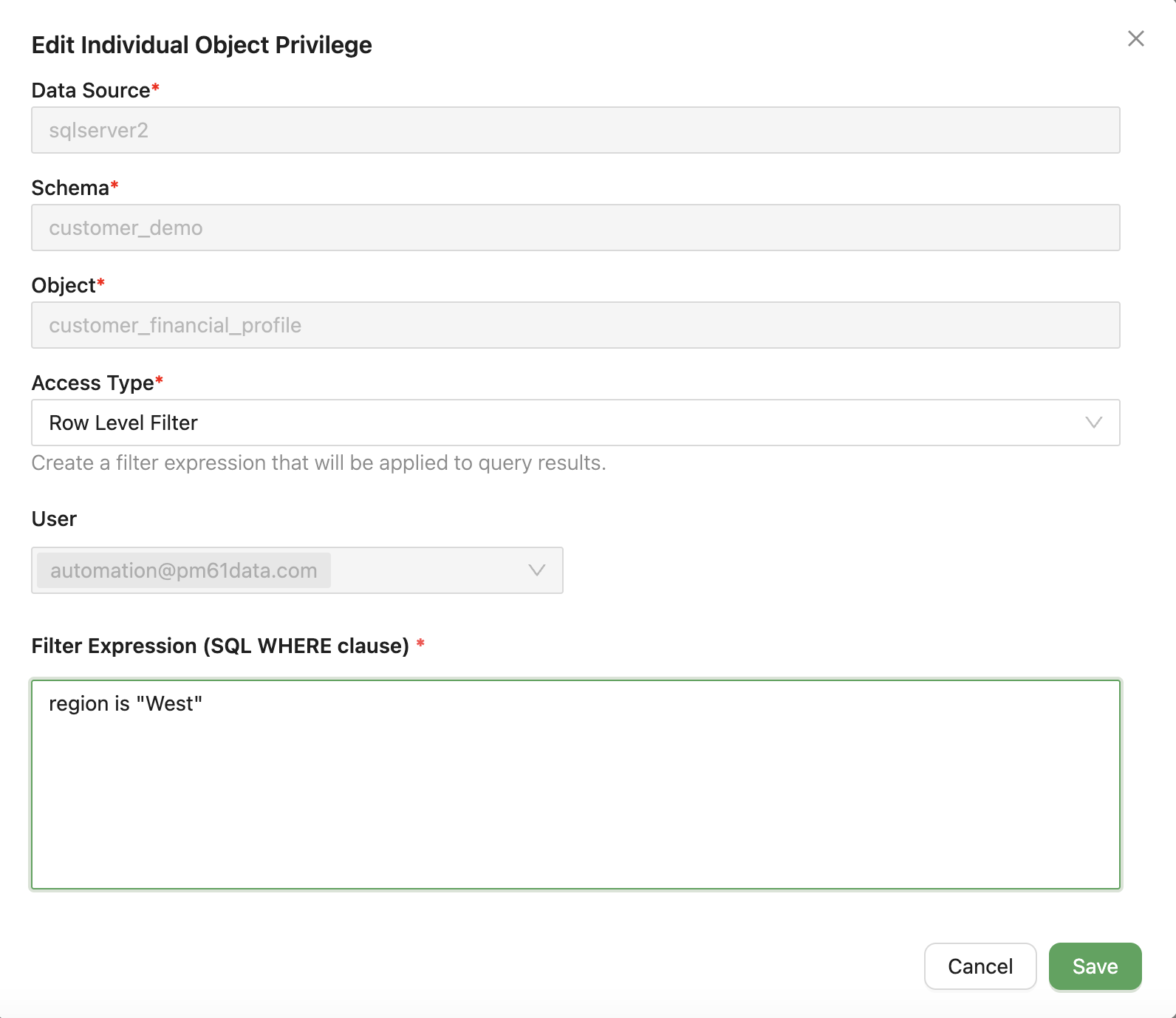
- Navigate to Data Authorization menu item
- Select the Users or Roles tab
- Choose the user or role to configure
- Click + Add Individual Object Privilege or edit an existing object
- In the Row Level Filter section, define the filter expression
- Use SQL WHERE clause syntax to specify the filter condition
- Click Save
Example Row Filters:
-- Filter by region for regional managers
region = 'WEST'
-- Filter by date range
transaction_date >= DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE, 90)
-- Combination filter
customer_segment = 'ENTERPRISE' AND region IN ('EAST', 'CENTRAL')
Row Filter Behavior
- Transparent to users - Filters applied automatically at query time
- Multiple filters - User sees union of all applicable filters
- Owner bypass - Object owners see all rows
- Performance - Filters pushed down to data source when possible
Column-Level Filtering
Control which columns users can see within a table or datamap.
What is Column-Level Filtering?
Column-level filtering restricts access to sensitive columns, showing masked values.
Configuring Column Filters
From Data Authorization Interface:
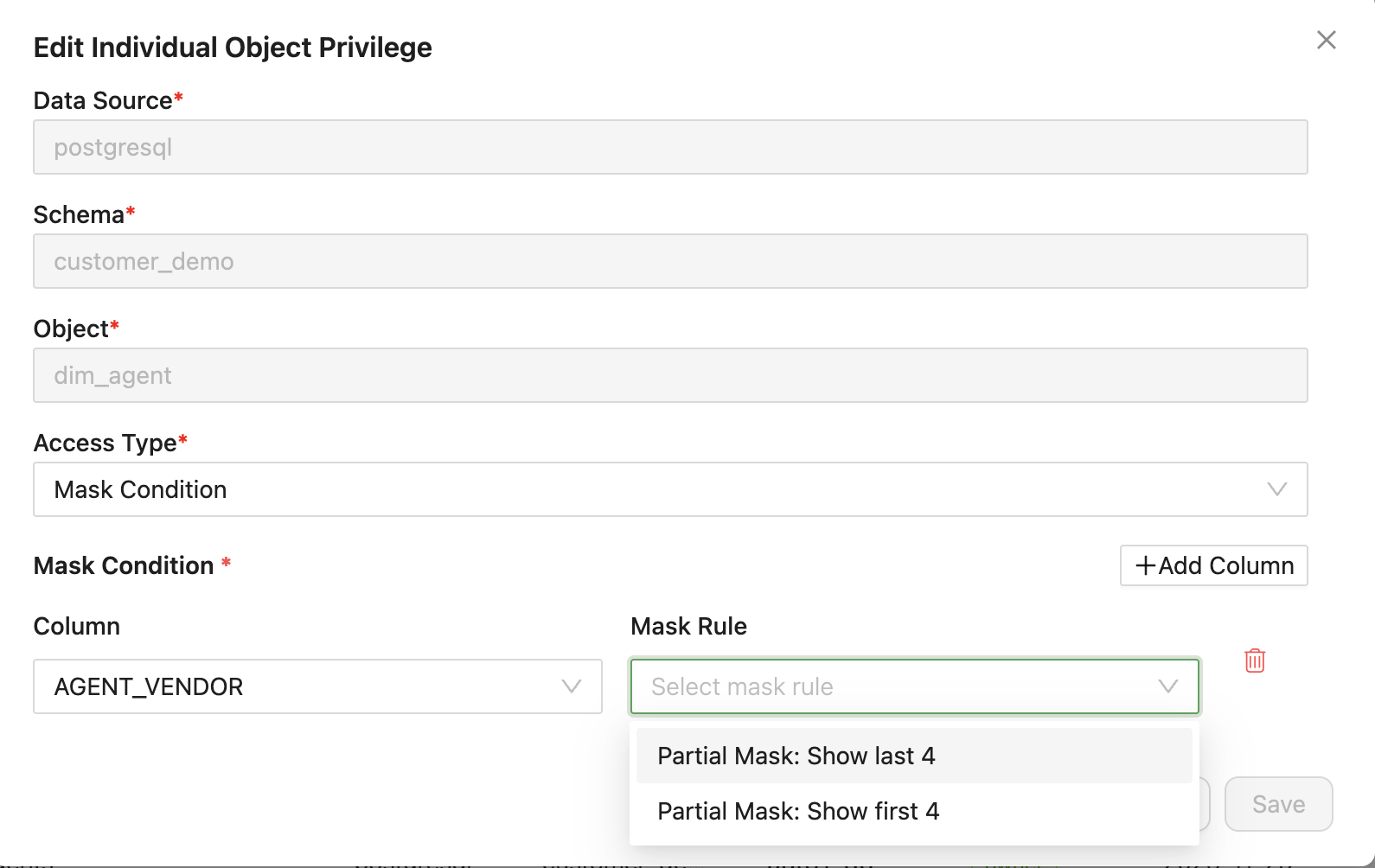
- Navigate to Data Authorization menu item
- Select the Users or Roles tab
- Choose the user or role to configure
- Click + Add Individual Object Privilege or edit an existing object privilege
- In the Mask Condition section, click + Add Column
- Select the column to mask from the dropdown
- Choose the Mask Rule (e.g., "Partial Mask: Show last 4", "Partial Mask: Show first 4")
- Click Save
Column Mask Rules
The system supports masking sensitive column data:
- Partial Mask: Show last 4 - Shows only the last 4 characters (e.g., for account numbers)
- Partial Mask: Show first 4 - Shows only the first 4 characters (e.g., for identifiers)
Combining Filters
Row and column filters work together to provide comprehensive data access control. When both are configured:
- Row filters limit which records a user can see
- Column filters control which fields are visible within those records
- Both are applied automatically when users query the data
Permission Resolution
When multiple access grants exist, Promethium checks these sources in order and grants the highest access level found:
- Object Ownership - Creators automatically have Owner access (cannot be revoked, only transferred)
- Direct Object Grant - Access explicitly granted on the object's Access Control tab
- Domain-User Privilege - Access inherited from object's domain membership
- Domain-Role Assignment - Access inherited from user's role's membership and objects domain membership
- Default - No access if none of the above apply
Access level precedence: Owner > Editor > Viewer
Example:
User: Alex
- Direct grant: Viewer
- Domain (via User): Editor
- Domain (via Role): Viewer
Result: Editor (highest level found)
Managing Object Permissions
Viewing Object Permissions
To see who has access to a specific object, open it and navigate to the Access Control tab.
Troubleshooting
User Cannot Access Object
Diagnosis Steps:
-
Check application permission:
- Does user's role include required Permission Set?
- Example:
create_datamappermission to work with datamaps
-
Check object-level permission:
- Is user the owner?
- Does user have the right Data Authorization privilege via a role or a domain?
Unexpected Access
If a user has access but shouldn't:
- Check for direct object grants
- Review Role assignments
- Verify object's Domain assignment
- Review recent permission changes in audit logs
Row/Column Filters Not Working
Troubleshooting:
- Verify filter syntax - Test SQL WHERE clause separately
- Review filter assignment - Confirm filter applies to user's role
- Test with owner access - Owners may bypass filters by default
- Examine query logs - Verify filter applied in executed query